
In this case, since 25 represents 1/4th of 100, two hal-life cycles must have passed in 1,000 years, since Let's say you started with 100 g and ended up with 25 g after 1,000 years.

Sometimes, if the numbers allow it, you can work backwards to determine an element's half-life. So, the initial mass gets halved every 7.72 years.
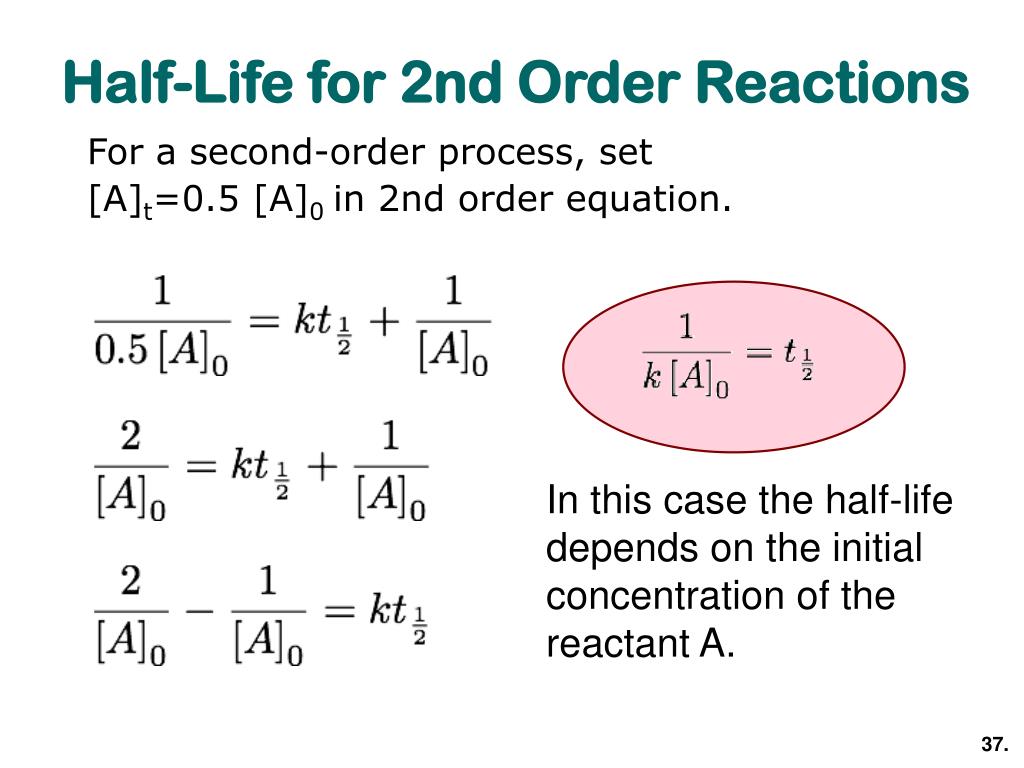
Half-lives can be a short as a fraction of a second or as long as billions of years. Each radioactive nuclide has its own half life. #98.0/t_("1/2") = log_(0.5)(0.000149) = 12.7# Half Life The half-life of a radioactive substance is the time interval during which half of a given number of radioactive nuclei decay and half remains un-decay. Here's how you would determine its half-life: It started from a mass of 67.0 g and it took 98 years for it to reach 0.01 g. Let's say you have a radioactive isotope that undergoes radioactive decay. So, if a problem asks you to calculate an element's half-life, it must provide information about the initial mass, the quantity left after radioactive decay, and the time it took that sample to reach its post-decay value. #t_("1/2")# - the half-life of the decaying quantity. evaluate natural-logarithm powers on your calculator (for many calculators. ChemMod: Posts: 21504: Joined: Thu Aug 04.
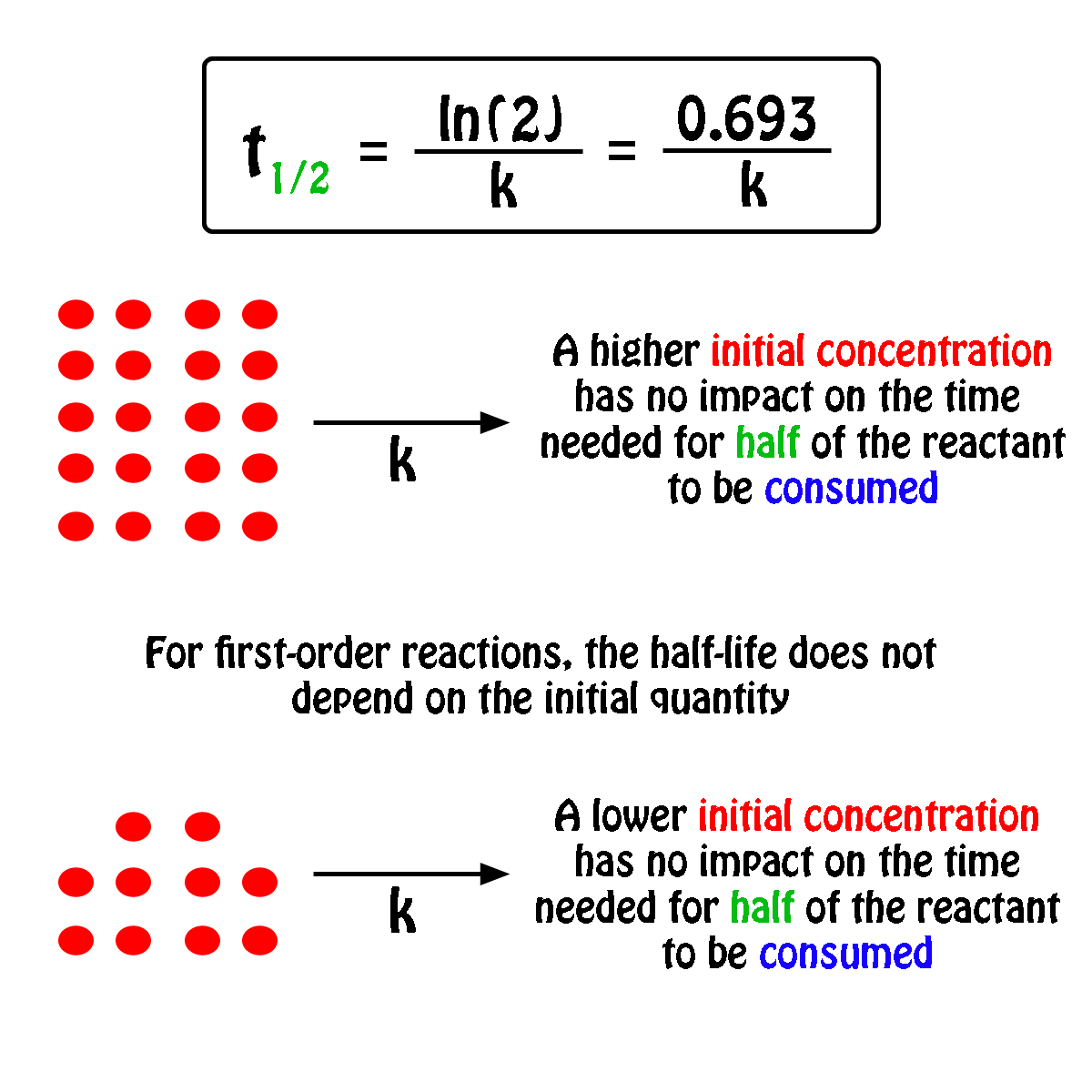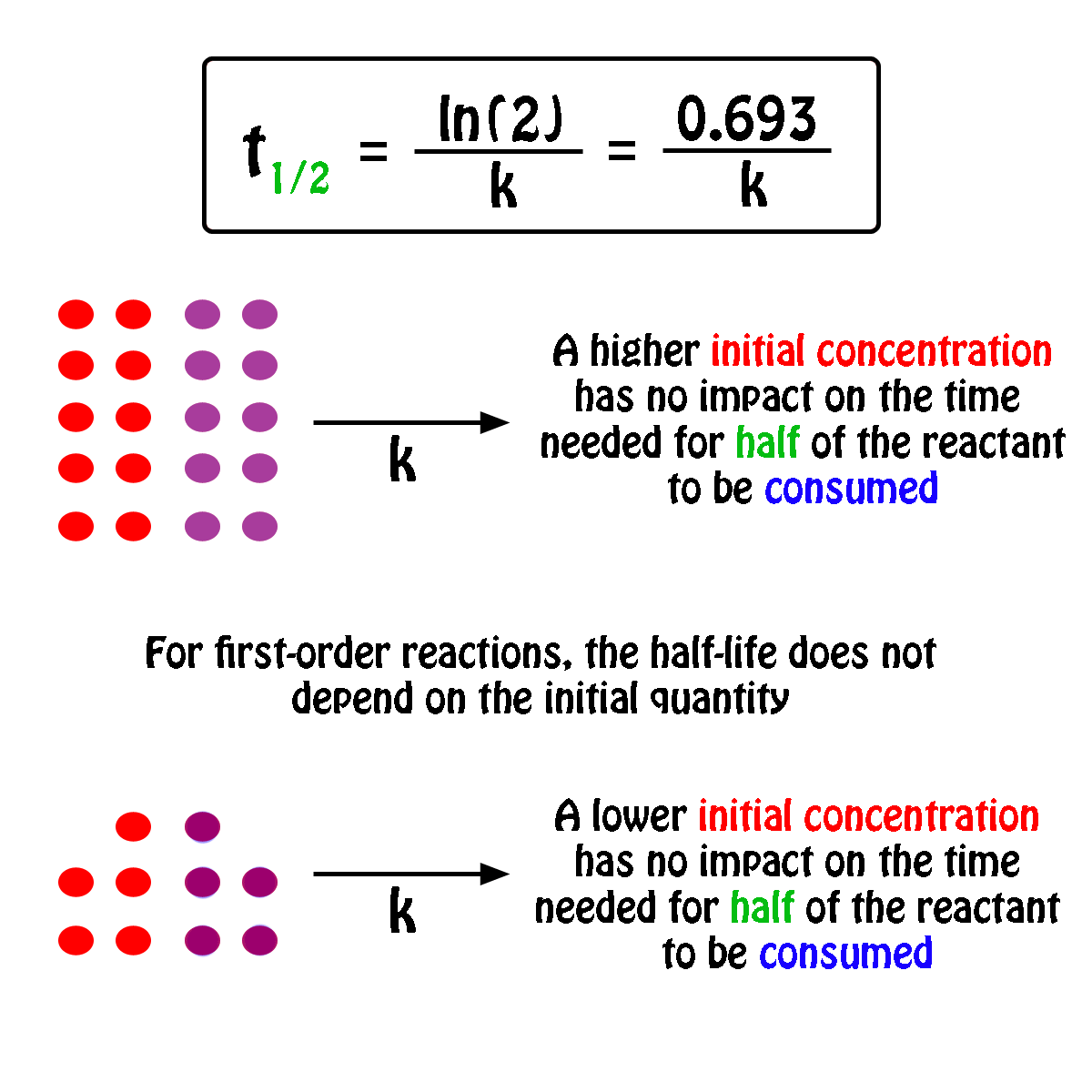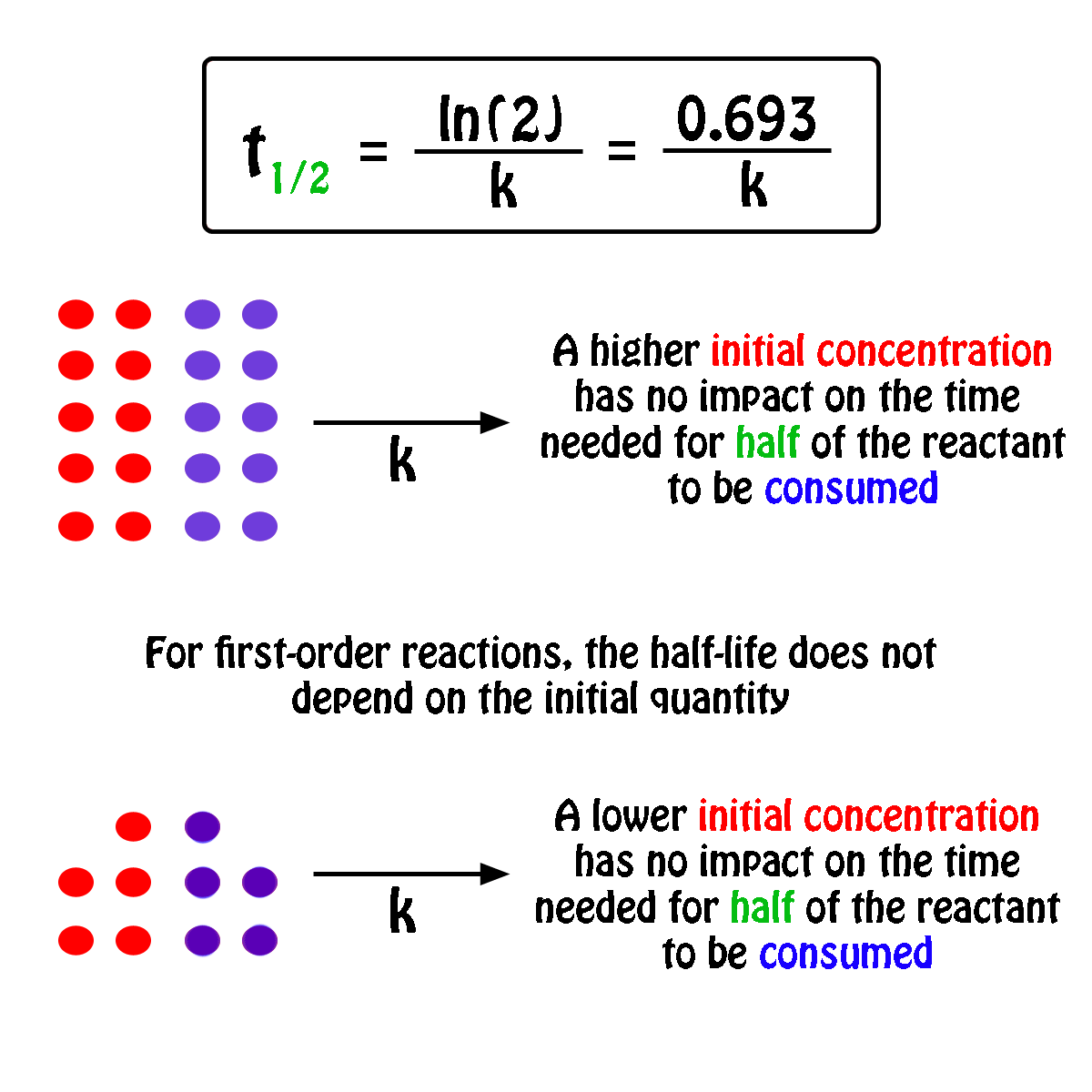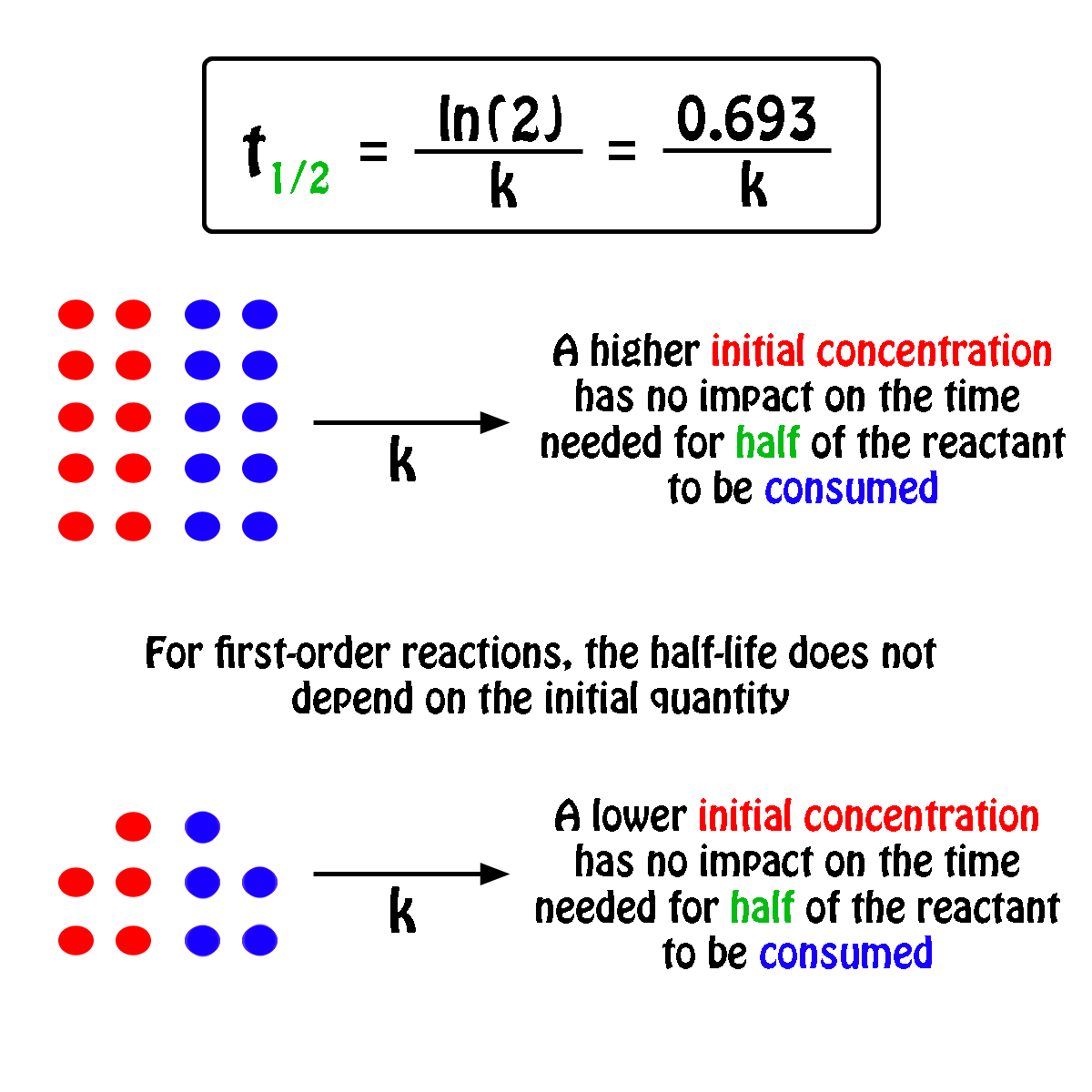
#A_0# - the initial quantity of the substance that will undergo decay An interesting and useful aspect of radioactive decay is half-life, which is. When we are calculating half-lives should we use the expression ln(2) in our calculator or use. Exponential decay can be expressed mathematically like this: The formula for calculating how many half-lives have passed is simple: H = L/2^t where H= number of half-lives and L= initial amount (in this case 100 g).Nuclear half-life expresses the time required for half of a sample to undergo radioactive decay. For example, if you had 100 grams of hydrogen and left them alone for one year, you would end up with 50 grams at the end of that time-since each atom decays into an atom of helium (usually) in a matter of minutes. In other words, if you have 100 atoms of some substance, that number will decrease by half every half-life. Half-life is the time it takes for a given quantity to decrease to half its initial value. The half-life of a given radioactive element is a constant, regardless of the conditions in which it is measured (temperature, pressure), or whether it’s being created as an unstable atomic nucleus splits up into two smaller nuclei (“decay”), or if you’re talking about something that’s already been around forever.
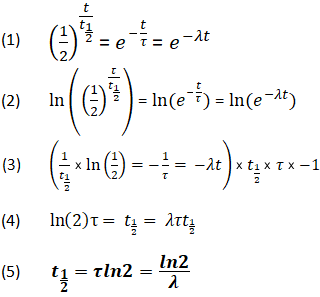
The half-life of radioactive material is the time it takes for half of the material to decay. The half-life of a substance is the time it takes for that substance to decrease to half its initial amount.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
